Goal
The GAIA project aims to explore Gaussian processes for efficient detection and interpretation of anomalies in multivariate time series data. In particular, we aim to investigate unsupervised Gaussian processes in order to identify, understand and resolve underlying correlations and anomalies. In order to learn Gaussian process models in a scalable and real-time manner, we intend to develop new streaming algorithms, which will be implemented in an open source manner and with reference to industrial standards, and tested in application-oriented scenarios, together with industry partners.
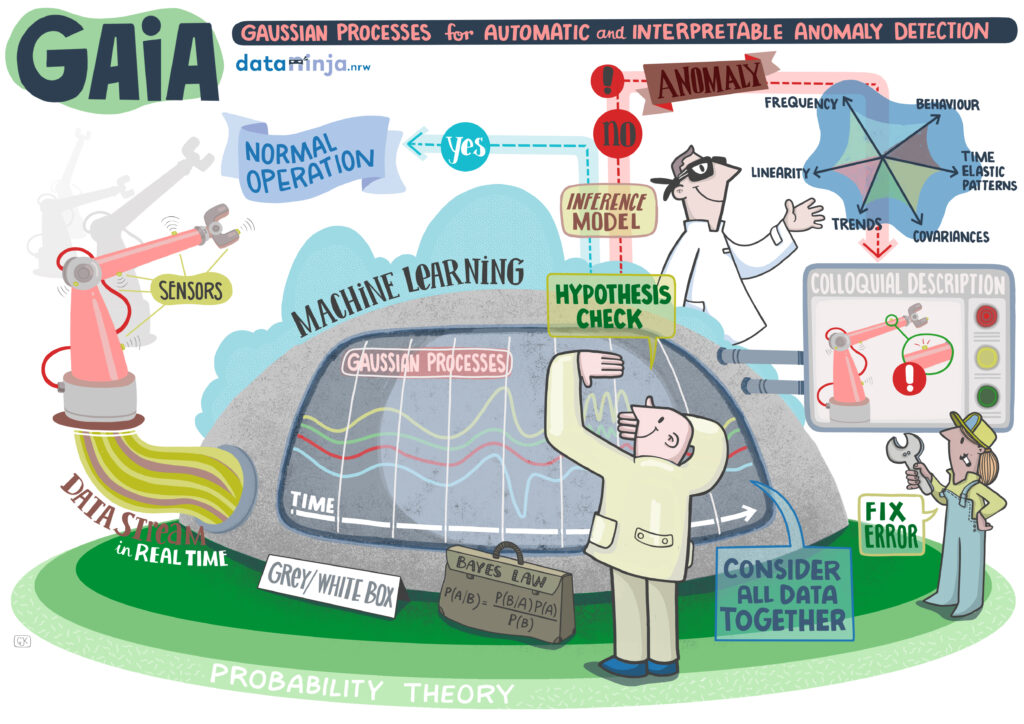
Project Overview
Gaussian Process Models are widely used in Bayesian Machine Learning as they can be applied when only limited data is available and can be directly interpreted. The GAIA project will employ such Gaussian Process Models in an extension to multivariate time series. The resultant model will therefore cover spatial as well as temporal information and should detect anomalies spanning both of these dimensions. On focus will be on how model selection influences the explainability of constructed models.
A latent variable model can be used, for example, to represent a process as is found in many industrial applications. Such processes are characterized through temporal data given as time series. In the project, a latent variable model should be learned in an unsupervised fashion as a Gaussian Process Model. Importantly, prior knowledge on the particular application domain can be exploited: While usually in Gaussian Processes the search for a fitting covariance function is expensive, domain knowledge can be introduced into the covariance matrix in the form of underlying differential equations which leads to hybrid and interpretable models.
During the first year, we managed to produce first results and a first implementation for physical data driven hybrid Gaussian Processes. Further, we supervised a successful Bachelor’s thesis on model selection, whose results we will further investigate.
Finally, we developed a novel model search algorithm for Gaussian processes on data streams and published a first evaluation.
1–4
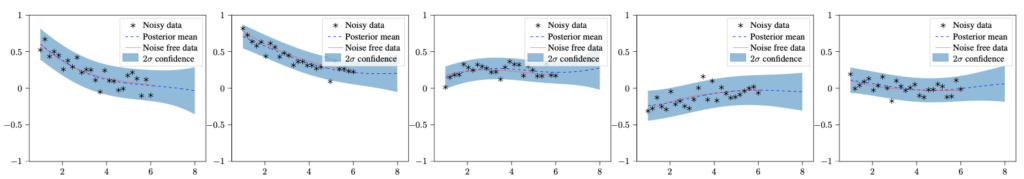
Project Publications
- Berns, Fabian, Jan David Hüwel, and Christian Beecks (2021). ‘‘LOGIC: Probabilistic Machine Learning for Time Series Classification’’. In: ICDM. IEEE, pp. 1000–1005.
- Berns, Fabian, Jan David Hüwel, and Christian Beecks (2022). ‘‘Automated Model Inference for Gaussian Processes: An Overview of State-of-the-Art Methods and Algorithms’’. In: SN Comput. Sci. 3.4, p. 300.
- Besginow, Andreas, Jan David Hüwel, Markus Lange-Hegermann, and Christian Beecks (2021). ‘‘Exploring Methods to Apply Gaussian Processes in Industrial Anomaly Detection’’. In: KI. Vol. 44.
- Besginow, Andreas, Jan David Hüwel, Markus Lange-Hegermann, and Christian Beecks (2024). ‘‘Finding commonalities in dynamical systems with gaussian processes’’. In: DataNinja sAIOnARA Conference, pp. 26–28. doi: 10.11576/dataninja-1162.
- Besginow, Andreas, Jan David Hüwel, Thomas Pawellek, Christian Beecks, and Markus Lange-Hegermann (2024). ‘‘On the Laplace Approximation as Model Selection Criterion for Gaussian Processes’’. In: arXiv preprint arXiv:2403.09215.
- Besginow, Andreas and Markus Lange-Hegermann (2022). ‘‘Constraining Gaussian Processes to Systems of Linear Ordinary Differential Equations’’. In: Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Ed. by Alice H. Oh, Alekh Agarwal, Danielle Belgrave, and Kyunghyun Cho.
- Gresch, Anne, Jana Osthues, Jan D Hüwel, Jennifer K Briggs, Tim Berger, Ruben Koch, Thomas Deickert, Christian Beecks, Richard KP Benninger, and Martina Düfer (2024). ‘‘Resolving spatiotemporal electrical signaling within the islet via CMOS microelectrode arrays’’. In: Diabetes, db230870.
- Hüwel, Jan David and Christian Beecks (2023). ‘‘Gaussian Process Component Mining with the Apriori Algorithm’’. In: DEXA (2). Vol. 14147. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer, pp. 423–429.
- Hüwel, Jan David and Christian Beecks (2024a). ‘‘Discovering Structural Regularities in Time Series via Gaussian Processes’’. In: DSAA. IEEE, pp. 1–10.
- Hüwel, Jan David and Christian Beecks (2024b). ‘‘Frequent Component Analysis for Large Time Series Databases with Gaussian Processes’’. In:EDBT. OpenProceedings.org, pp. 617–622.
- Hüwel, Jan David, Fabian Berns, and Christian Beecks (2021). ‘‘Automated Kernel Search for Gaussian Processes on Data Streams’’. In: IEEE BigData. IEEE, pp. 3584–3588.
- Hüwel, Jan David, Andreas Besginow, Fabian Berns, Markus Lange-Hegermann, and Christian Beecks (2021). ‘‘On Kernel Search Based Gaussian Process Anomaly Detection’’. In: IN4PL (Revised Selected Papers). Vol. 1855. Communications in Computer and Information Science. Springer, pp. 1–23.
- Hüwel, Jan David, Anne Gresch, Tim Berger, Martina Düfer, and Christian Beecks (2022). ‘‘Analysis of Extracellular Potential Recordings by High-Density Micro-electrode Arrays of Pancreatic Islets’’. In: DEXA (2). Vol. 13427. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer, pp. 270–276.
- Hüwel, Jan David, Anne Gresch, Fabian Berns, Ruben Koch, Martina Düfer, and Christian Beecks (2022). ‘‘Tracing Patterns in Electrophysiological Time Series Data’’. In: DSAA. IEEE, pp. 1–10.
- Hüwel, Jan David, Florian Haselbeck, Dominik G. Grimm, and Christian Beecks (2022). ‘‘Dynamically Self-adjusting Gaussian Processes for Data Stream Modelling’’. In: KI. Vol. 13404. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer, pp. 96–114.
- Hüwel, Jan David, Georg Stefan Schlake, Kevin Albrechts, and Christian Beecks (2024a). ‘‘Discovering Propagating Signals in High-Content Multivariate Time Series via Spatio-Temporal Subsequence Clustering (In print)’’. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Big Data.
- Hüwel, Jan David, Georg Stefan Schlake, Kevin Albrechts, and Christian Beecks (2024b). ‘‘Identifying Propagating Signals with Spatio-Temporal Clustering in Multivariate Time Series’’. In: SISAP. Vol. 15268. Lecture Notes in Computer Science. Springer, pp. 207–214.
- Schlake, Georg Stefan, Jan David Hüwel, Fabian Berns, and Christian Beecks (2022). ‘‘Evaluating the Lottery Ticket Hypothesis to Sparsify Neural Networks for Time Series Classification’’. In: ICDE Workshops. IEEE, pp. 70–73.
Cooperation
References
- 1.F. Berns, K. Schmidt, I. Bracht, C. Beecks. 3CS Algorithm for Efficient Gaussian Process Model Retrieval. In: Proceedings 25th of the International Conference on Pattern Recognition 2020. IEEE Computer Society; 2021:1773-1780. https://www.uni-muenster.de/forschungaz/publication/164365
- 2.Lange-Hegermann M. Algorithmic Linearly Constrained Gaussian Processes. In: S. Bengio, H. Wallach, H. Larochelle, K. Grauman, N. Cesa-Bianchi, R. Garnett, eds. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vol 31. Curran Associates, Inc.; 2018. https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2018/file/68b1fbe7f16e4ae3024973f12f3cb313-Paper.pdf
- 3.F. Berns, C. Beecks. Complexity-Adaptive Gaussian Process Model Inference for Large-Scale Data. In: Proceedings of the SIAM International Conference on Data Mining (SDM 2021). ; 2021.
- 4.Beecks C, Willy Schmidt K, Berns F, Gra A. Gaussian Processes for Anomaly Description in Production Environments. In: Papotti P, ed. Proceedings of the Workshops of the EDBT/ICDT 2019 Joint Conference, EDBT/ICDT 2019, Lisbon, Portugal, March 26, 2019. Vol 2322. CEUR-WS.org; 2019. http://ceur-ws.org/Vol-2322/dsi4-4.pdf


